International Coconut Genebank
INTRODUCTION
To increase the economic value of coconut product and incone of the farmers diversification products of copra and oil must be produced such as: dessicated coconut, coconut milk, oleochemical, carbon active, coir, dust of husk, and etc. In this case, coconut farmers and processors will need new varieties. The new coconut varieties can be developed through breeding activities. To have a successfull breeding program we should have genetic variabilities in the breeder's collection of material or germplasm collection.
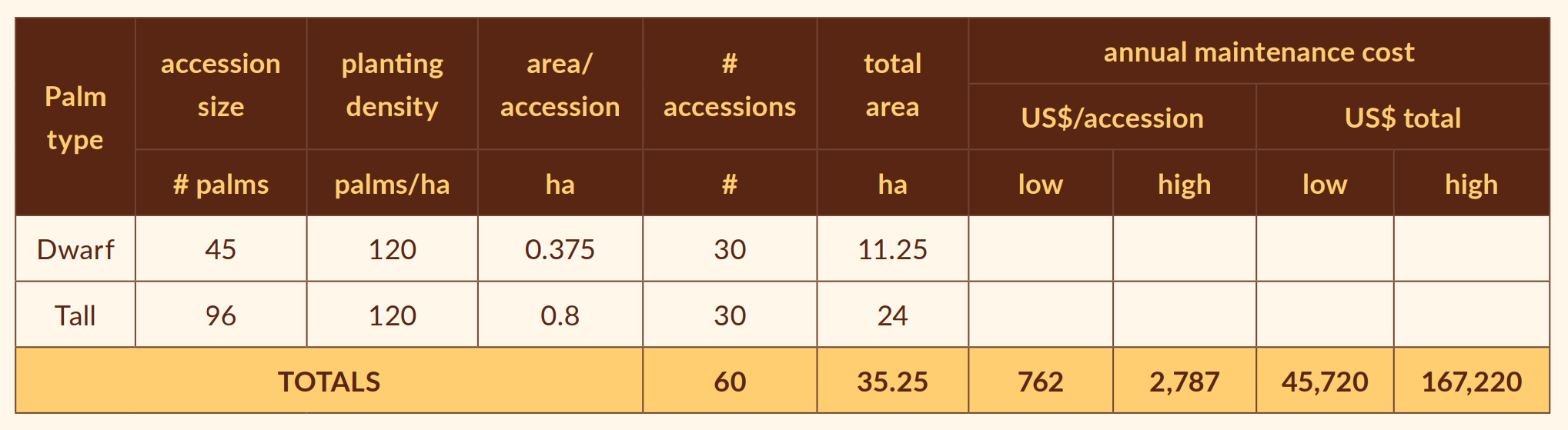
Coconut seeds are recalcitrant (cannot survive drying or freezing) so cannot be stored. Each genotype must beplanted in field genebanks, or their tissue or pollen frozen, as an ‘accession’. Because of their reproductive nature, each accession normally comprises 45 palms (for dwarf-types) to 96 palms (for tall types). So, coconut field genebanks require greater area and are more costly to maintain. For a coconut field genebank with 30 accessions of each type, it will need at least 35ha for accessions, excluding nursery buildings and experimental plots. In 2013 estimates of the annual cost per accession varied between US$762 (COGENT) and US$2,787, so a 60-accession genebank would annually cost anything between US$46K and US167K (Global Strategy, 2018). The collections in Côte d’Ivoire, Indonesia and PNG are being moved to new sites, and a recent estimate for moving the ICG-AIO over an 8-year period came to over US$15 million for 59 accessions. Costs seem generally higher in Africa than in Asia.
There are five International Coconut Genebanks (ICGs), established in the 1990s in Brazil, Côte d’Ivoire, India, Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. In common with many of the 19 national collections, all five ICGs face several challenges that constrain germplasm exchange.
Previous surveys indicate that overall ICG management and capacities need strengthening, and they suffer from accessions’ mislabelling, threats from pests and climate-change, land tenure issues, poor germplasm data management, lack of human and other resources, including financial support, and are in desperate need of upgrading, especially in terms of rejuvenation, backup, and collecting new material.
For an international collection to be ratified, the host government signs a tripartite ‘Article 15’ agreement with both the FAO-International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (ITPGRFA) and the COGENT host organisation (now the ICC), to hold the collection as a global public good to be accessible within the multilateral system of germplasm exchange, and to effectively maintain and protect the collection. New agreements for all 5 ICGs are being drafted, to accommodate COGENT’s new host, the ICC.
Further to the abovementioned Treaty, another agreement has also been signed between COGENT and its member counties on the provision of sharing germplasm with their designated ICGs. This agreement needs to be renewed, as the agreements signed previously have automatically expired after the COGENT was moved from Bioversity International to ICC in year 2019. In 1999, COGENT which was previously under Bioversity International, has established five International Gene Banks (ICGs) across the Globe designating five member countries as the “Host Country”namely;
- ICG-SEA (for South East and East Asia) in Indonesia
- ICG-SAME(for South Asia and Middle East) in India
- ICG-SP for South Pacific in PNG
- ICG-AIO (for Africa & Indian Ocean) in Ivory Coast
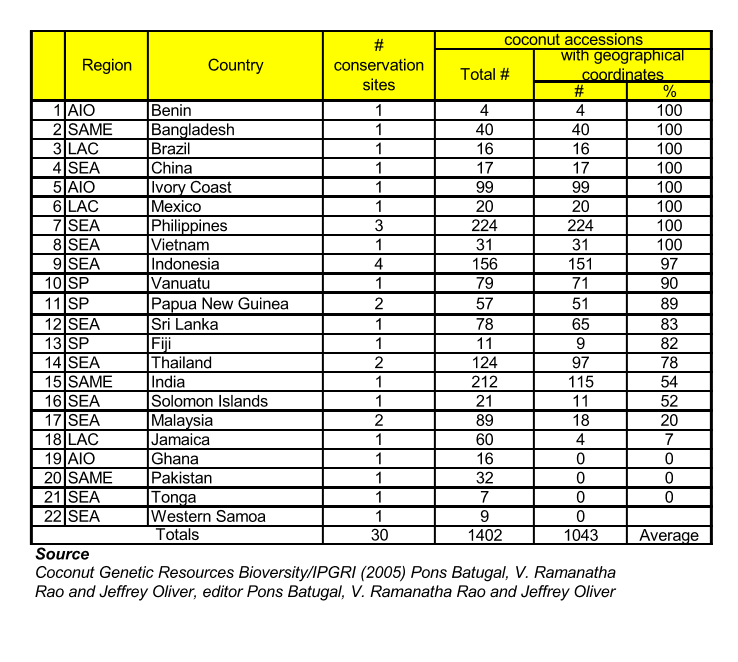
- ICG-LAC (for Latin America & Caribbean) in Brazil More than 1,000 coconut accessions representing more than 400 cultivars are now conserved within these International Coconut Genebanks (ICGs) and in 19 other National Coconut Genebanks (NCGs) established by COGENT member countries across the world. The aim is to support in optimizing the conservation and use of as much representative coconut diversity as possible
LIST OF ICG's ACCESSIONS 2005